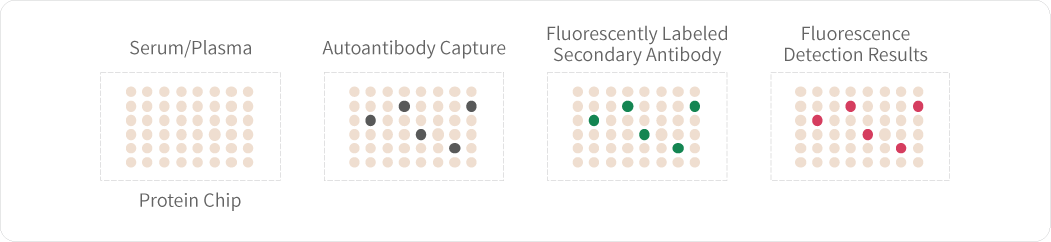
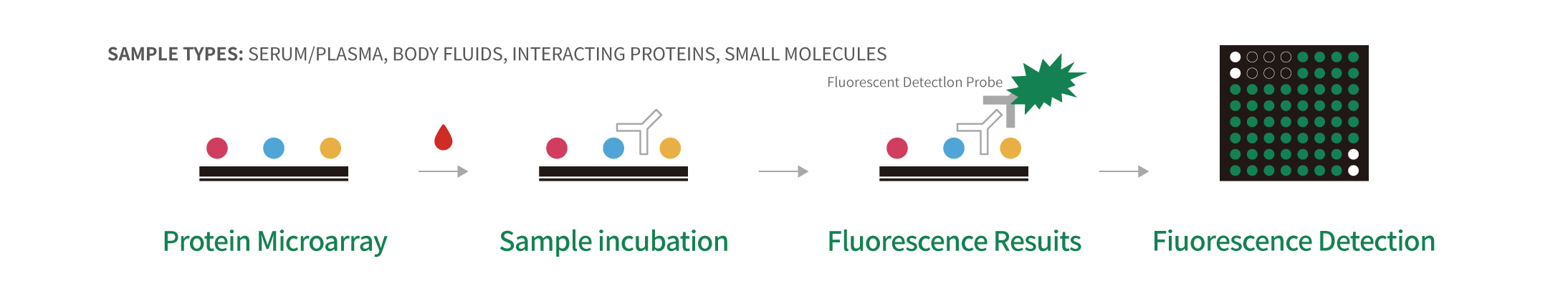
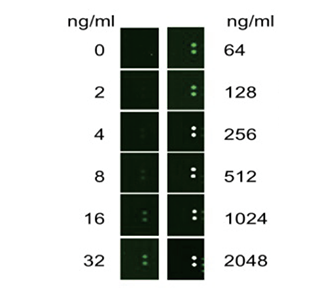
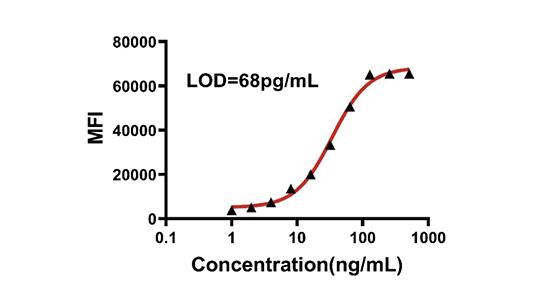
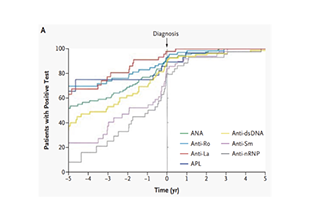
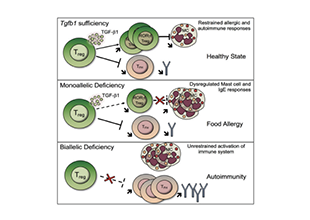
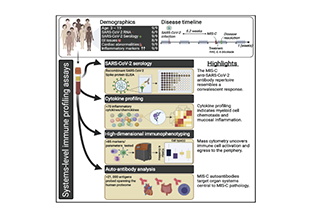
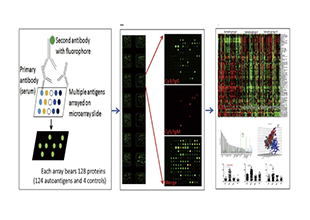
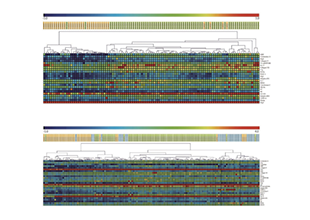
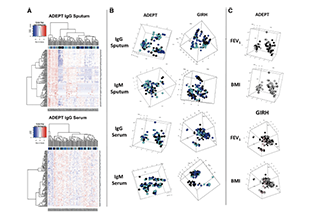
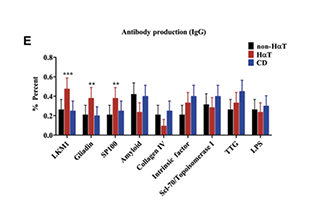
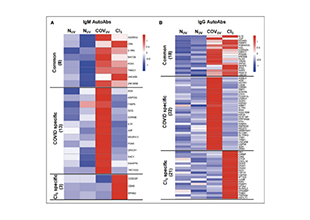
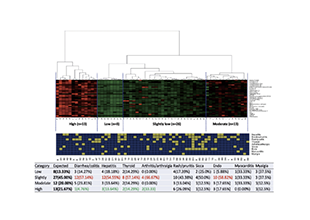
Autoantibodies are a class of antibody molecules secreted by the B-cell immune system that can recognize self-proteins.
They play a crucial role in maintaining the homeostasis of organisms, distinguishing between normal and abnormally proliferating cells, and in immune system disorders. Given their important physiological functions, identifying the target antigens of these autoantibodies and elucidating their clinical applications in the diagnosis and treatment of tumors, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders have significant value.